Understanding Psoriasis: A Holistic Look Through Western Medicine, Ayurveda, Naturopathy, and Gut Health
Understanding Psoriasis: A Holistic Look Through Western Medicine, Ayurveda, Naturopathy, and Gut Health
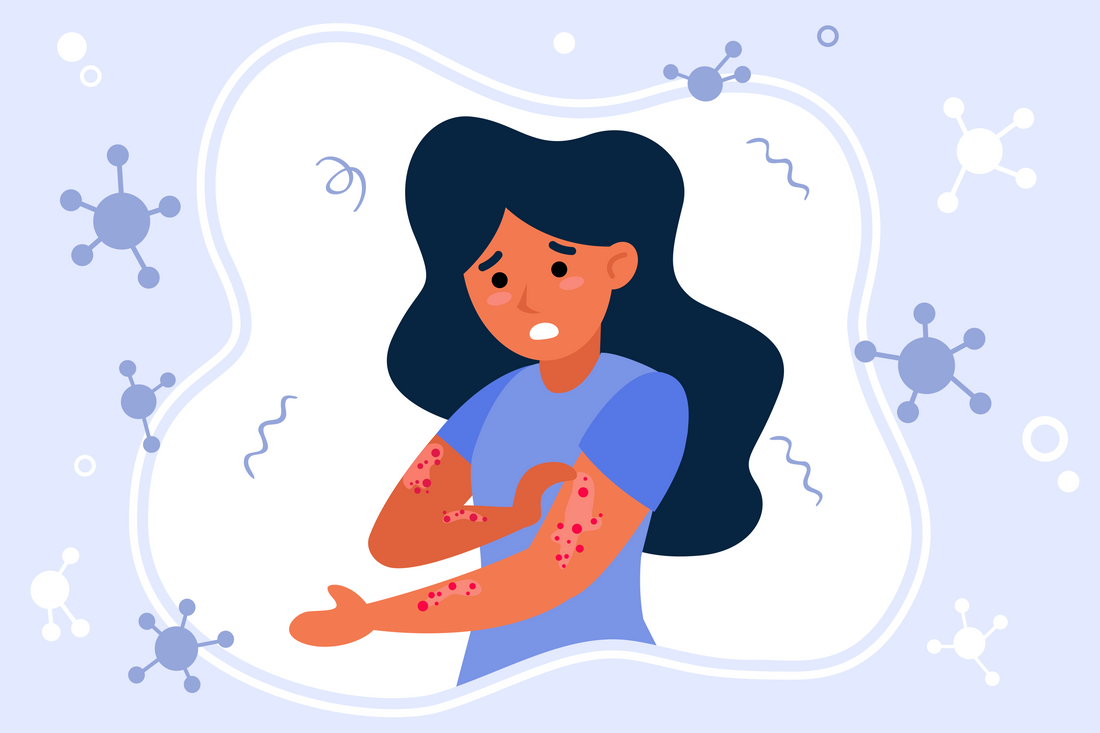
Psoriasis is more than a skin condition, it’s a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects millions globally. Characterized by red, scaly patches on the skin, psoriasis is often misunderstood as merely cosmetic. However, its roots run deeper, involving complex interactions between the immune system, genetic predispositions, environmental triggers, and increasingly, gut health.
While Western medicine typically approaches psoriasis with immunosuppressants and topical therapies, ancient systems like Ayurveda and naturopathy view it through a more holistic lens.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition where skin cells multiply up to 10 times faster than normal. This results in the buildup of skin cells, forming plaques that are often itchy, inflamed, and painful. There are several types of psoriasis, including:
Plaque psoriasis (most common)
Guttate psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis
Inverse psoriasis
Erythrodermic psoriasis (rare and severe)
Psoriasis is often triggered by factors like stress, infections, certain medications, or trauma to the skin.
Western Medicine Approach
Strengths:
Relief through topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and biologics
Systemic treatments (like methotrexate or cyclosporine) for moderate to severe cases
Targeted biologics that modulate specific immune pathways (e.g., IL-17, TNF-α inhibitors)
Limitations:
Focuses on symptom suppression, not root causes
Long-term side effects of immune-modulating drugs
Often overlooks the role of diet, lifestyle, and gut health
Ayurvedic View on Psoriasis
In Ayurveda, psoriasis is categorized under "Kushtha" (skin diseases), specifically as Eka Kushtha. It is believed to result from an imbalance in the three doshas: Vata, Pitta, and Kapha, with Pitta and Kapha predominance. The accumulation of Ama (toxins) due to improper digestion is considered a root cause.
Ayurvedic Treatments:
Internal detoxification: Panchakarma therapies like Vamana (emesis) and Virechana (purgation)
Herbal remedies: Neem, turmeric, Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia), and Khadirarishta
Diet and lifestyle: Avoiding spicy, sour, fermented foods and focusing on Sattvic diet
Stress reduction through meditation, yoga, and pranayama
Ayurveda focuses on individualized treatment, long-term balance, and internal healing.
Naturopathic Medicine Perspective
Naturopathy views psoriasis as a manifestation of internal imbalances, particularly involving detoxification organs like the liver, kidneys, and intestines. It emphasizes functional medicine approaches and treats the person, not just the disease.
Common Naturopathic Strategies:
Elimination diets to identify food sensitivities (gluten, dairy, nightshades)
Liver support with herbs like milk thistle and dandelion
Anti-inflammatory nutrition: Omega-3s, leafy greens, turmeric
Stress and adrenal support
Detoxification protocols
Naturopathic doctors often link psoriasis with leaky gut syndrome, microbial imbalances (dysbiosis), and systemic inflammation.
The Gut-Skin Connection: Why Gut Health Matters
In recent years, scientific research has increasingly supported the gut-skin axis—a bidirectional relationship between gut microbiota and skin health. People with psoriasis often have:
Increased intestinal permeability (leaky gut)
Altered gut microbiota (reduced diversity)
Systemic inflammation linked to poor gut health
Supporting Gut Health:
Probiotics and fermented foods (sauerkraut, kimchi, kefir)
Prebiotics (fiber-rich foods to feed good bacteria)
Avoiding gut irritants (alcohol, sugar, processed foods)
Healing nutrients like L-glutamine, zinc, and collagen
Improving gut health may reduce autoimmune flare-ups and improve overall immunity, which is crucial in managing psoriasis.
Integrative Strategies for Healing Psoriasis Naturally
Mind Your Diet: Eliminate potential triggers, eat anti-inflammatory, and support gut repair.
Manage Stress: Use meditation, yoga, or therapy to reduce cortisol and immune dysregulation.
Detox Safely: Support liver and kidney function naturally to reduce toxic load.
Balance the Microbiome: Use probiotics, fiber, and avoid antibiotics unless necessary.
Customize Your Care: Work with integrative or functional practitioners for personalized plans.
Psoriasis is a complex condition that benefits from a multi-dimensional approach. Western medicine offers powerful tools for symptom control, but when combined with the deep healing insights of Ayurveda, the natural detoxification focus of naturopathy, and modern understanding of gut health, patients often find more sustainable relief and greater well-being.
If you’re navigating psoriasis, consider exploring these integrative approaches, not as a replacement for medical care, but as complementary tools in your healing journey.
Disclaimer:
This blog is for educational and informational purposes only and is not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any disease. The Ayurvedic and herbal information shared here reflects traditional knowledge and is not a substitute for professional medical advice. Always consult a qualified healthcare provider before starting any new diet, supplement, or lifestyle program, especially if you have a medical condition, are pregnant or nursing, or are taking prescription medications.
Image Credit: pch.vector / Freepik
References:
Damevska K, França K, Lotti T, Nikolovska S, Pollozhani N. Complementary and integrative therapies for psoriasis: Looking forward. Dermatol Ther. 2018 Sep;31(5):e12627. doi: 10.1111/dth.12627. Epub 2018 Aug 22. PMID: 30133906.
Ljubenovic M, Lazarevic V, Golubovic M, Binic I. Integrative Approach to Psoriasis Vulgaris. Holist Nurs Pract. 2018 May/Jun;32(3):133-139. doi: 10.1097/HNP.0000000000000180. PMID: 29261515.
Tirant M, Lotti T, Gianfaldoni S, Tchernev G, Wollina U, Bayer P. Integrative Dermatology - The Use of Herbals and Nutritional Supplements to Treat Dermatological Conditions. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. 2018 Jan 21;6(1):185-202. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.041. PMID: 29484023; PMCID: PMC5816298.